Decipher cell death linked to mitochondrial toxicity
Cytotoxicity and mitochondrial toxicity induced by compounds often trigger irreversible cellular injury leading to cell death. Mitologics’ technological platform MiToxView® offers assays to investigate cell death parameters on primary and differentiated cell types.
Although cell death is necessary to eliminate damaged and excessive cells, maintain homeostasis and healthy tissues, an accumulation of dead cells within a tissue can induce serious organ dysfunction. Cell death manifests with macroscopic morphological alterations, characteristic of the pathway triggered. There are three major forms of cell death: apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy.
To explore any toxicity of compounds and anticipate potential side effects, it is important to evaluate cell death morphology and the related cascade of biochemical events.
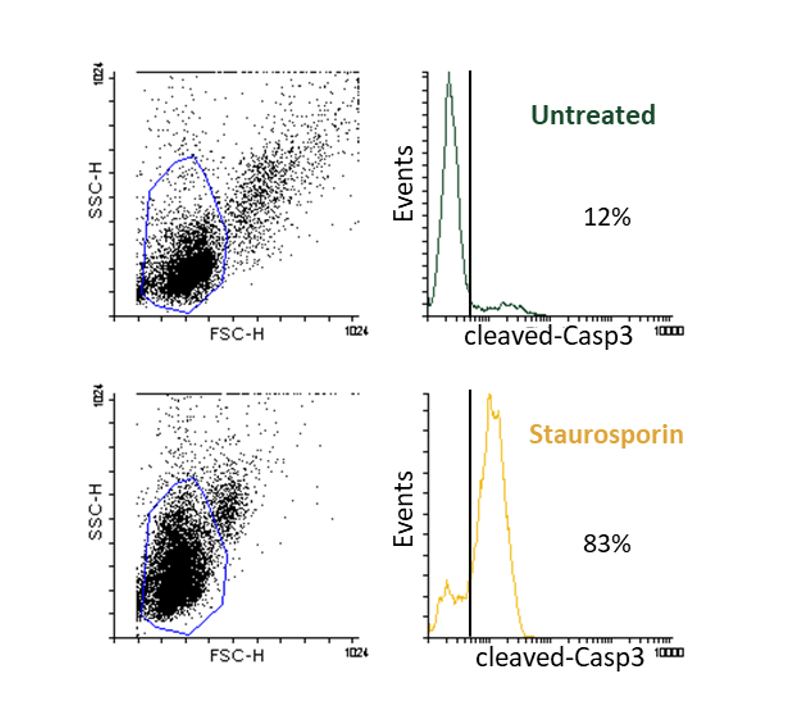
Detect cell death hallmarks in Human blood cells.
Induction of apoptosis after acute treatment of PBMC freshly isolated from human blood, with compounds of interest. Mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis (caspase-3 cleavage) is measured by flow cytometry.
Hallmarks of apoptosis can also be detected in patient samples during clinical trial.
By assessing cell death parameters on primary and differentiated cell types with our MiToxView® platform, the consolidated data produced can help you to:
- Identify compounds displaying severe mitochondrial toxicity,
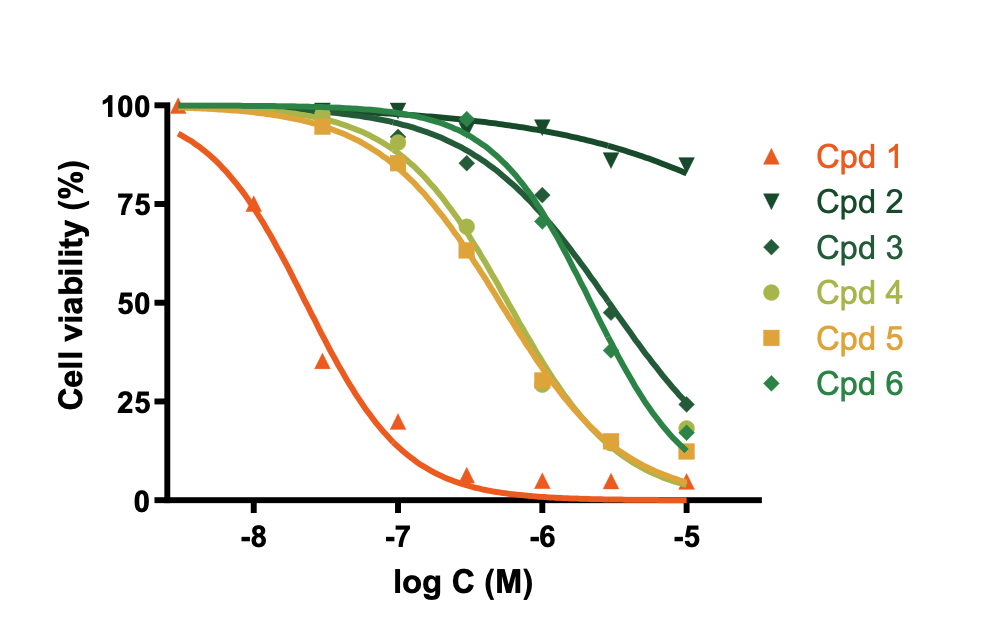
- Screen and rank compounds based on their impact on cell viability,
- Understand the cell death pathway triggered by a compound: apoptosis, necrosis, autophagy,
- Predict a compound’s toxicity in humans: hepatotoxicity/DILI, cardiotoxicity, etc.,
- Analyse cellular damage in pre-clinical and clinical biological samples.