Early detection of potential drug-induced cardiotoxicity due to mitochondrial damage and elucidation of the underlying mechanisms
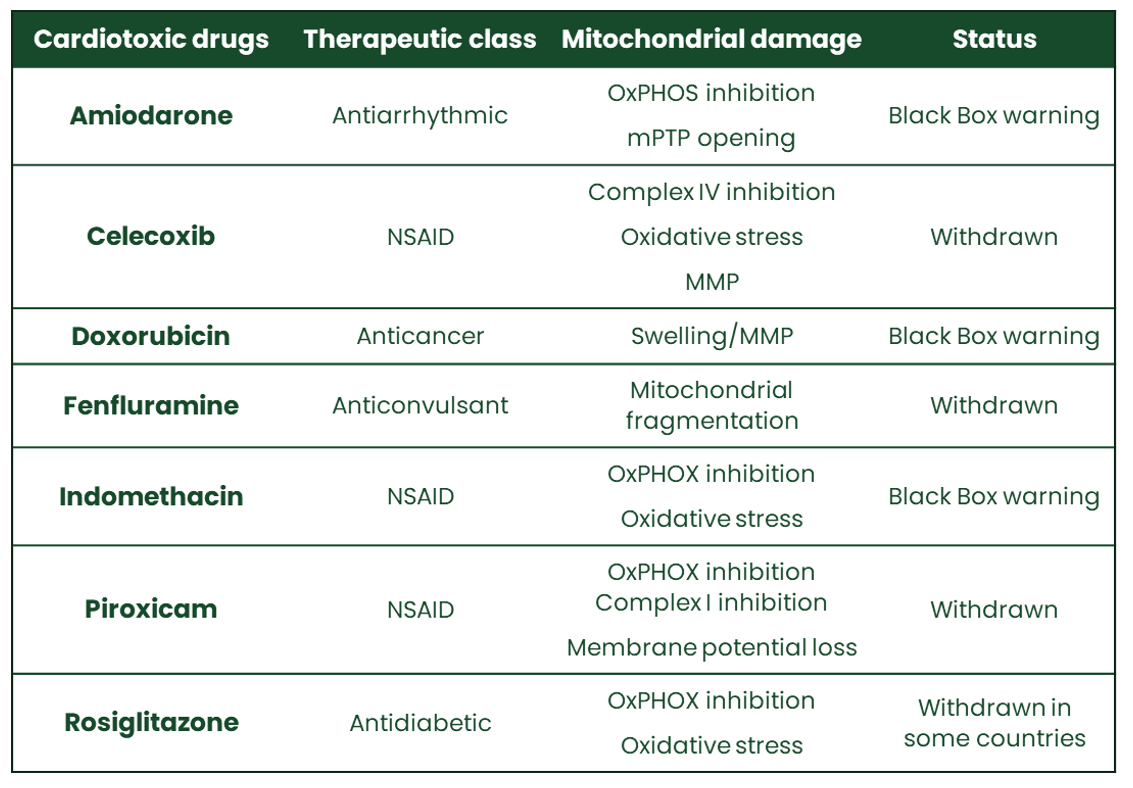
In the clinic, drug-induced cardiotoxicity has been observed with all therapeutic drug classes and is one of the most serious noted side effects. Drug-induced cardiac injury related to mitochondrial damage leads to discontinuation of clinical trials, boxed warning, or even withdrawal of approved drugs.
It is crucial to anticipate these risks early, before drugs reach advanced clinical phases to ensure patient health and reduce candidate attrition. The MiToxView® platform proposed by Mitologics is designed to identify cardiotoxicity risks due to mitochondrial damage at an early stage.
In the clinic, drug-induced cardiotoxicity can often be attributed to mitochondrial dysfunction, through mitochondrial respiratory chain impairment, mitochondrial membrane permeabilisation (MMP) and/or oxidative stress.
Our MiToxView® platform offers a competitive range of assays on cardiac cells and isolated heart mitochondria (subsarcolemmal and/or intrafibrillar) from rodents, allowing you to detect drug-induced mitochondrial damage early in your process. Our tests are useful to identify mitochondriotoxic drugs that might induce acute and long-term cardiotoxicity, and also shed light on the underlying mechanisms.
With MiToxView®, drug-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and its detrimental consequences can be characterised by assessing: