Investigate mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (MMP)
Any breach of mitochondrial membrane integrity – whether due to disease or as a result of exposure to a drug or compound – can cause cell death.
The technological platforms MitoPathway® and MitoXpert® developed by Mitologics provide robust assays to measure mitochondrial membrane permeabilisation.
Identify mitochondrial target of compounds such as Permeability Transition Pore (mPTP).
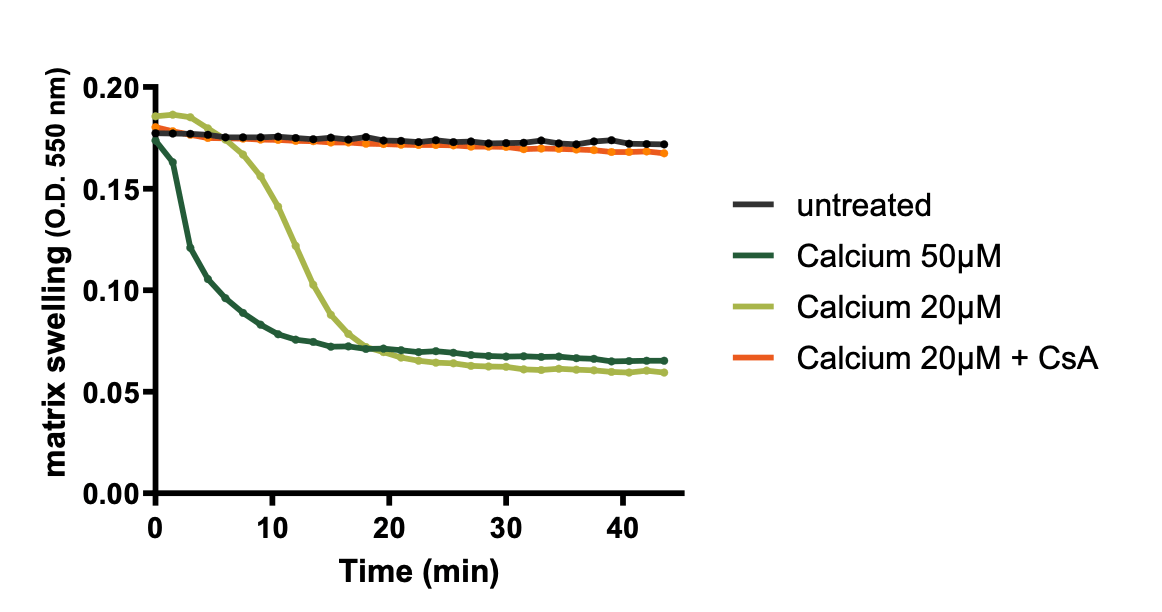
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mtPTP) assay performed on isolated mouse liver mitochondria. Calcium-dependent mPTP opening induces a mitochondrial swelling monitored by spectrophotometry during 45 min (OD 550 nm) and inhibited by cyclosporin A (CsA, cyclophilin D inhibitor).
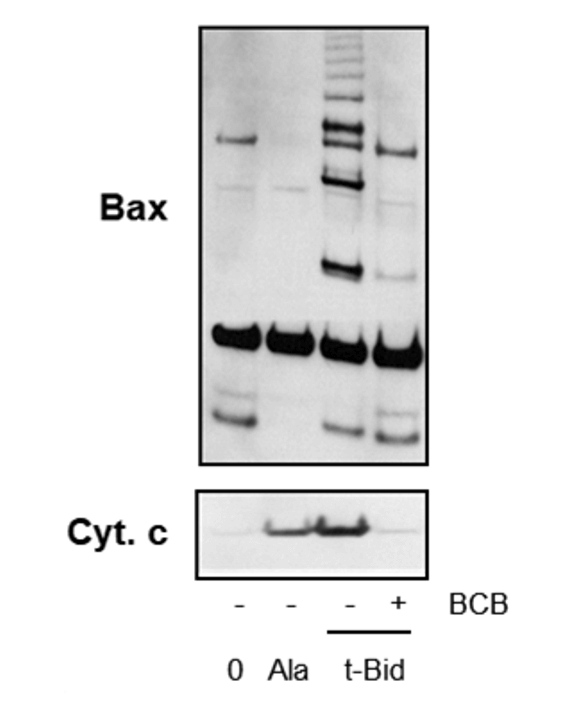
Multiple exchanges between the matrix, the intermembrane space and the cytosol take place at the inner (IMM) and outer (OMM) mitochondrial membranes, governed by the modulation of membrane protein complexes forming translocases, pores, and channels. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilisation (MOMP) is a key mechanism involved in apoptotic cell death, associated with the formation of Bax/Bak oligomers in the outer mitochondrial membrane. MOMP leads to cytochrome c release, triggering caspase activation. The permeability transition pore (mPTP) is another contributor to mitochondrial membrane permeabilisation (MMP). Sensitive to calcium and ROS overload, mPTP opening leads to necrotic cell death but can also be regulated by Bax/Bak proteins.
Cell death in acute myocardial infarction or neuronal injury has been linked to Bax/Bak channel formation and mPTP opening. In contrast, inhibition of these pathways by Bcl-2 family anti-apoptotic proteins in cancer cells is associated with tumour resistance. Thus, MMP modulators represent interesting therapeutic strategies that can be identified and explored through mitochondria-based assays to determine their mode of action (MoA).
Identify mitochondrial target of compounds such as pro-apoptotic Bax/Bak channels.
Pro-apoptotic Bax/Bak pore opening assay performed on isolated tumor mitochondria. Oligomerization of Bax/Bak and release of cytochrome c by the recombinant t-Bid protein were revealed by Western Blot (or Elisa) and inhibited by Bax Channel Blocker (BCB) (Buron et al., 2010).
Our MitoPathway® and MitoXpert® platforms provide consolidated data to help you to:
- Identify potential mitochondrial targets of compounds, and the various components involved, such as Permeability Transition Pores (mPTP) or Bax/Bak channels,
- Measure a direct protective effect on mitochondria subjected to calcium overload, oxidative stress or apoptotic triggers used to induce MMP,
- Discover or validate the mode of action of MMP inducers, such as Bcl-2 targeting and mPTP openers,
- Highlight pro-apoptotic compounds that induce MOMP specifically in tumour cells (Buron et al., PloS One, 2010). For this application, the differential screening assay uses healthy and tumour mitochondria to reveal series of compounds targeting Bcl-2 family proteins, with a tumour-selective toxicity profile that preserves healthy cells.